Introduction to Letters of Credit | 2024 Guide
Letter Of credit
Welcome to Abelsoro trading Letters of Credit hub. Find out how we can help you access Letters of Credit to increase your imports and exports to guarantee the payment and delivery of goods. Or, discover the latest research, information and insights on Letters of Credit here.

What is a Letter of Credit (LC)
Letters of credit (also know as documentary credits) are payment instruments that constitute a definite undertaking of the issuer (“the issuing bank”) on the instruction of the buyer (“applicant”) to pay a certain specified amount to a seller (“the beneficiary”) at sight or on a future determinable date (“the maturity date”) provided that documents stipulated in the letter of credit/documentary credit are presented in compliance with the stated terms and conditions.
The issuing bank issues the documentary credit on behalf of its customer (“the applicant”) or on its own behalf.
These undertakings are known as “documentary credits”, as they specify the documents that must be presented in order for the credit to be honoured.
These are also known as “letters of credit” (LCs) as they were originally issued in a physical document form addressed to the beneficiary with the issuing bank’s undertaking to pay upon receipt of complying documents.
Here are several key aspects of documentary credits (letters of credit):
1. Irrevocability: Once issued, a documentary credit is irrevocable, meaning the issuing bank cannot alter or cancel it without the agreement of all relevant parties—namely, the issuing bank, the beneficiary, and any confirming bank.
2. Documentary Nature: Payments under documentary credits depend on the submission of specified documents in accordance with the credit’s terms. The payment obligation is contingent upon the correct presentation of these documents.
3. Compliance: Payment is only made when the documents presented by the beneficiary meet the terms and conditions of the credit. If there are discrepancies, the issuing bank can refuse payment unless the discrepancies are corrected before the credit expires or unless the applicant waives the discrepancies and the issuing bank agrees to accept them.
4. Payment Mechanism: Documentary credits serve as a payment method to facilitate trade transactions. They ensure that the beneficiary (seller) gets paid while the applicant (buyer) receives the goods or services. This mechanism helps fulfill the buyer’s payment obligations as outlined in the underlying contract.
5. Independence and Autonomy: Documentary credits operate independently from the underlying contract. The issuing bank’s and any confirming bank’s obligations are separate from the terms of the sale or contract. This principle of autonomy is outlined in the ICC Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits 2007 Revision (UCP 600), which is recognized globally.

Purpose
The purpose of a documentary credit is to provide a mechanism or arrangement to facilitate the settlement of an international or domestic trade transaction by use of a bank undertaking.
It should be noted that banks only deal with documents and not with goods, services or performance to which the documents may relate.
The terms and conditions of a documentary credit form the basis upon which the applicant must reimburse an issuing bank when a complying presentation is made.
Documentary credits assure the beneficiary of payment as long as they present the requisite complying documents to the nominated bank, the confirming bank (if any), or the issuing bank.
Diagram: How does a Letter of Credit work?
The normal LC process flow can be diagrammatically represented as follows:
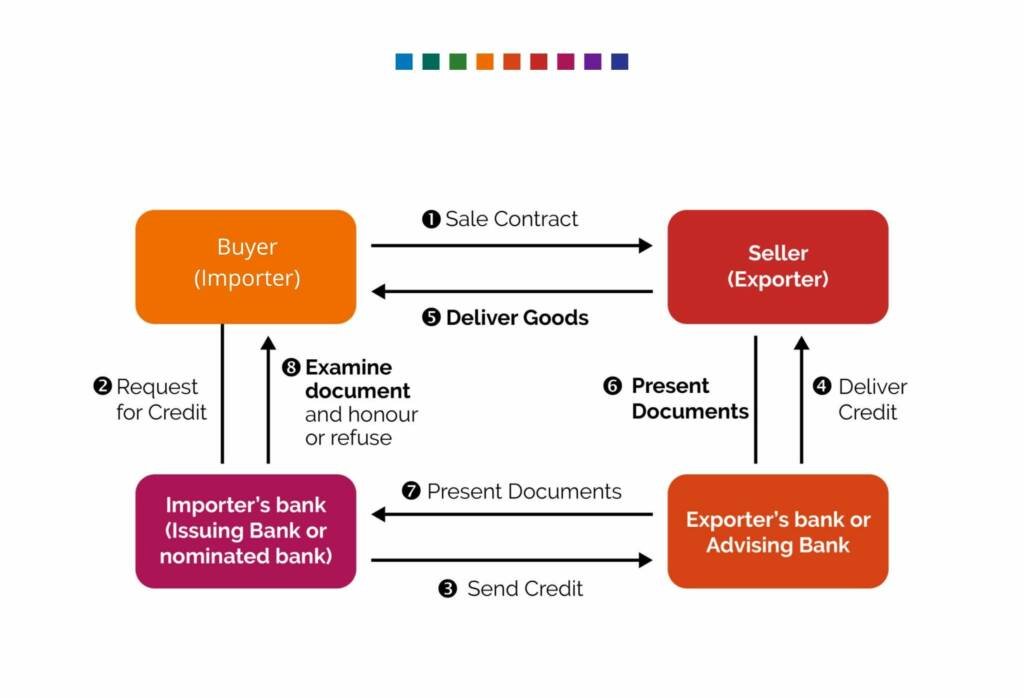
Diagram: Letter of Credit Issuance & Settlement